LunarBot Hardware User Manual
1.0 Introduction
A lunar rover is a robotic vehicle designed to traverse the rocky surface of the Moon. The LunarBot is the fundamental unit of a lunar service robot cluster, developed by the Distributed and Intelligent Space System Lab (DSSL) at Tsinghua University.
This uncrewed robotic rover is designed for data collection and lunar terrain photography. Its robust design features a 4-wheeled independent steering and driving platform, a comprehensive multi-modal perception system, and a sophisticated 7-degree-of-freedom manipulator for interaction with the lunar environment.
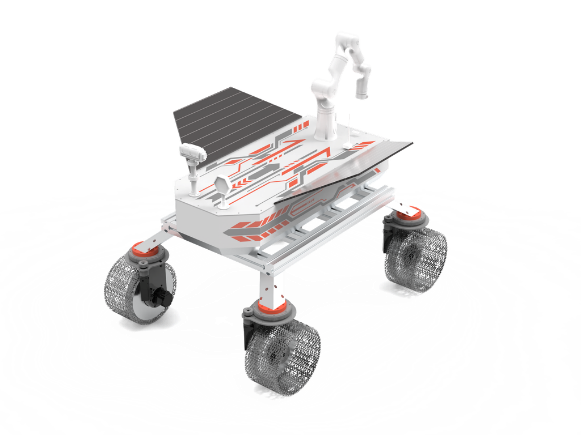 Figure 1: The LunarBot Robotic Rover Concept
Figure 1: The LunarBot Robotic Rover Concept
 Figure 2: The LunarBot Robotic Rover
Figure 2: The LunarBot Robotic Rover
2.0 Geometric Specifications
| Dimension | Value (mm) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Length | ≈ 1303.05 | Without solar panels and manipulator |
| Width | ≈ 997.09 | Without solar panels and manipulator |
| Height | ≈ 782 | Without solar panels and manipulator |
| Wheel Diameter (Φ) | 260 | Without EVA foam |
| Wheel Width | 168 |
3.0 Component Overview
3.1 Wheel Assemblies
The LunarBot features four identical, independently controlled wheel assemblies. Each wheel unit contains the following components:
- Driving Motor: 200 Watts motor with an integrated encoder for precise velocity and position control.
- Steering Motor: 100 Watts motor with an integrated encoder for accurate angular positioning.
- Origin Indicator Sensor: An NPN switch for homing the steering mechanism.
- Limitation Indicator Sensor: An NPN switch to prevent mechanical over-rotation.
- Gear Boxes: Dedicated gear boxes for both the steering and driving motors to achieve optimal torque.
- Note: The servos (motor controllers) for these motors are installed within the main chassis chamber.
3.2 Chassis Chamber
The sealed chassis chamber houses the core power and electronic systems:
- Power System:
- High-Voltage Graphene Power Cell (Primary drive power)
- Low-Voltage Graphene Power Cell (Primary drive power)
- Control System:
- 8 Servos: Motor controllers for the 4 driving and 4 steering motors.
- Computation Module: The main onboard computer for processing sensor data and executing commands.
- Safety:
- Circuit breakers for system protection.
3.3 Sensor Suite
The LunarBot is equipped with a multi-modal perception system for navigation and data collection:
- Livox-Mid360 LiDAR: A 360° LiDAR sensor for high-resolution 3D mapping and obstacle detection in the surrounding environment.
- Intel RealSense D435i Camera: A depth-sensing camera that provides RGB video, depth information, and inertial data for 3D vision, visual odometry, and terrain analysis.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Integrated within the RealSense camera, providing accelerometer and gyroscope data for tracking orientation and acceleration.
3.4 Manipulator System
For physical interaction and sample handling, the LunarBot is fitted with a robotic arm and gripper:
- Manipulator: Realman RM-75, a 7-Degree-of-Freedom (7-DOF) robotic arm, providing human-like dexterity for complex tasks.
- End Effector: Inspire Robots EG2-4C, a 2-finger gripper for grasping and manipulating objects.
4.0 Key Features
- All-Terrain Mobility: Four-wheel independent steering and driving allows for omnidirectional movement and precise positioning on challenging lunar terrain.
- Advanced Perception: Fusion of LiDAR, 3D vision, and IMU data enables robust autonomous navigation and mapping.
- Robotic Manipulation: The 7-DOF arm and gripper extend the rover's capabilities beyond mobility to active interaction with the environment.
- Robust Power System: Dual graphene power cells provide reliable and extended operational capacity.
Manufacturer: Distributed and Intelligent Space System Lab (DSSL), Tsinghua University.